How Cloud Computing is Reshaping the Fintech Industry?
- DevOps
- September 29, 2023
In today’s digital age, finance is rapidly evolving, thanks to the adoption of cloud computing in the fintech industry. This blog delves into the transformative power of cloud computing in fintech and its key trends, exploring how it’s reshaping financial services, from simplifying data management to offering personalized solutions.
Gone are the days when finance was connected to complicated jargon, required endless paperwork, and hours long time at brick-and-mortar banks. In this digital era, finance is evolving at breakneck speed, and the driving force behind this revolution is the adoption of cloud computing in fintech.
Cloud computing is not only changing the way we store our photos, documents, and data, but it’s reshaping the entire financial landscape. It can store, process, and deliver data and services over the internet that power up fintech companies. For us, it is creating a financial future that’s more accessible, efficient, and inclusive than ever before.
In this blog, we will analyze the role of cloud computing in the fintech industry. We will understand how it is reshaping the sector and changing dynamics from how we save and invest to how we make everyday payments.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a technology that enables companies, businesses, and individuals to access and leverage a varied range of computing resources and services over the Internet. The data is stored in a cloud instead of local servers or personal computers.
According to the reports, 85% of organizations will adopt cloud computing by 2025. 75% of enterprises are investing in cloud-native app development, and 4 out of 5 enterprises plan to increase cloud investment with time. Hence, by 2023, cloud adoption may generate $3 trillion in revenue before taxes, interest, depreciation, and EBITDA.
By using cloud services, users can tap into a shared pool of resources hosted in data centers and operated by cloud service providers. In a nutshell, with cloud computing, you don’t need to buy, install, and maintain a server.
Cloud services are divided into three main categories:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): It provides virtualized computing resources, including storage, virtual machines, and networking. Users have more control over the operating system and applications.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): The cloud type offers a platform and environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications. Developers can focus on writing code while the platform manages the underlying infrastructure.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): These cloud services deliver fully functional software applications. Users access the software through a web browser, eliminating the need for local installations.
Read also: IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Picking the Best Cloud Computing Service Model
Why is Cloud Computing Important for the Fintech Industry?
Cloud computing has given both financial companies and small fintech startups the tools to streamline their operations and change the way they work and operate. The technology allows them to use powerful computers and services without spending a lot of money upfront. So, instead of buying expensive computers and software upfront, they can rent what they need from the cloud and compete with reputed industry players.
Cloud computing also provides highly personalized financial services and simplifies meeting all the complex rules and regulations that financial companies must follow. In simple words, the technology has made Fintech more accessible, secure, and capable of meeting individual needs.
How Cloud Computing Has Transformed the Fintech Industry?
With its innovative approach and technical advancements, cloud computing has shaped the fintech industry positively. Below are some of the key transformations of cloud computing that have propelled the fintech industry’s growth forward.
Seamless Data Management
Cloud computing helps fintech organizations maintain variable data volumes and eliminate the blind spots of data silos, providing clean, organized, and contextualized data structures. Moreover, cloud-based data processing tools and platforms allow fintech firms to analyze and process data in real-time.
This capability is essential for tasks, including algorithmic trading, risk assessment & mitigation, fraud detection, data management, compliance monitoring, etc. Cloud platforms also provide tools and APIs for integrating data from various sources, allowing fintech firms to consolidate data from different sources to gain comprehensive insights.
Resource Optimization
Cloud service providers operate data centers worldwide and distribute their services geographically, allowing the fintech industry to use this global infrastructure. It ensures low-latency access for customers in different regions while optimizing the use of resources.
Cloud platforms provide access to automation tools that help fintech companies optimize resource distribution. For example, organizations can easily spin up or turn off virtual servers according to their preference and situation, ensuring optimal resource utilization without manual intervention.
Fintech firms can consolidate their infrastructure into the cloud if they have operated on multiple on-premises data centers in the past. The consolidation ensures proper use of all resources and reduces wastage.
Cost Efficiency
Cloud providers use a subscription-based pricing model, and fintech companies only pay for the resources and services they actually use. The facility abolishes the need for large upfront capital investments in hardware and infrastructure. In addition, cloud services leverage a multi-tenant model, allowing multiple customers to share the same physical infrastructure.
Resource pooling leads to economic benefits as the cost of infrastructure is distributed among multiple users. With cloud computing, companies also don’t pay for hardware maintenance, power consumption, cooling, physical server management, technical issue resolving, etc. This reduction in personnel costs contributes to overall cost efficiency.
Flexibility and Scalability
Cloud services offer scalable storage solutions, allowing firms to store and maintain large amounts of data without the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. If the data volume is large, fintech companies can easily expand their storage capacity in the cloud. In adverse circumstances, companies can lower the storage space and pay less for it.
Cloud computing ensures easy scale-up or scale-down for fintech businesses. Moreover, cloud services enable secure access to data from anywhere with an internet connection. Fintech professionals and customers can access financial information and services according to their requirements and irrespective of location.
Uptight Security
Cloud providers use robust security measures and take disaster preventive steps like access controls, threat detection, data encryption, security patching, data residency, auditing, and monitoring. Companies can protect sensitive and financial data using built-in security features and ensure uptight security for their business.
Along with it, cloud computing also provides automated data backup and disaster recovery solutions. Fintech companies can ensure data integrity and business continuity by regularly backing up data to the cloud and recovering it swiftly in case of disruptions.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Innovations in the Fintech Industry
At present, the exceeded growth of fintech companies is visible after adopting cloud computing. However, the technology has a lot more to offer in upcoming years. It will transform everything from money transactions to financial management. Here is a glimpse of this transformation.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), is a type of cloud computing. In this model, developers can build and run apps without managing the underlying infrastructure. It is better than the traditional server-based approach, where developers provision and manage servers, handle scalability, and monitor server conditions to run apps.
However, these serverless functions are stateless, and they don’t maintain information or state between invocations. Any required state is either stored in external databases or storage services.
Moreover, these serverless functions are designed to run for a short duration, often measured in milliseconds to a few minutes. Long-running processes are more suitable for other computing models.
Read also: Serverless Architecture for Cloud-based App Development: Top Benefits and Challenges
Containerization and Kubernetes
Containerization is an emerging cloud computing technology that enables developers to package an app and its dependencies, including configurations, runtime environment, libraries, etc., into a single unit called a container. These containers are isolated from each other and share the host operating system’s kernel, which makes them lightweight and efficient.
On the other hand, Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform for automating containerized applications’ deployment, scaling, and management. It offers a set of features for container orchestration, load balancing, scaling, self-healing, service discovery, rolling updates, extensibility, etc.
Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Strategies
A hybrid cloud is an IT environment that combines on-premises infrastructure (private cloud) with one or more public cloud providers. It allows data and applications to be shared between them. The cloud type helps with data security, compliance, handling spikes in demand, disaster recovery, testing, and development.
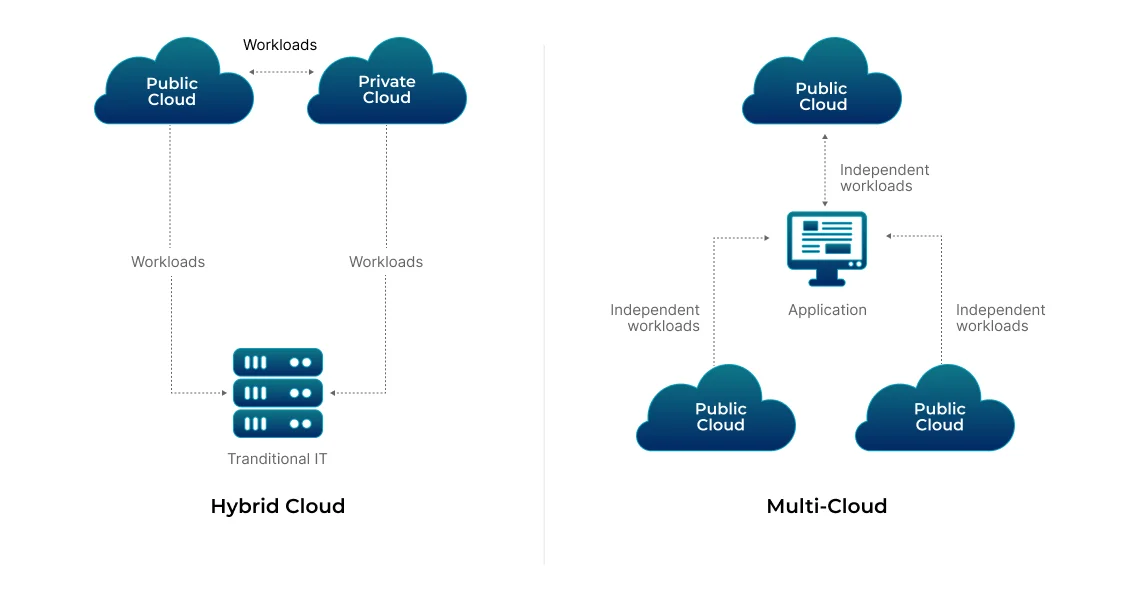
A multi-cloud strategy refers to using multiple public cloud providers to host different parts of an organization’s IT infrastructure. It requires an on-premises component. This cloud computing strategy helps with vendor diversity and choosing the best-suited cloud services, disaster recovery, and improving geographic redundancy.
Cloud Native Data Management
Cloud-native data management is a set of strategies, practices, and technologies used to manage data in cloud computing environments efficiently. Cloud technology is closely connected to the principles of cloud-native application development while prioritizing scalability, resilience, and agility. It will address unique challenges and opportunities that cloud infrastructure and applications often experience.
Data management in cloud-native environments emphasizes high availability and fault tolerance. The data is often replicated across multiple availability zones or regions to minimize downtime during crashes or failures.
Edge Computing for Low Latency
Edge computing is a divided computing model that contains computational resources and data storage closer to the location, near the network, or wherever they are needed. The technology does not rely on centralized cloud data centers.
It reduces latency issues, which is a major concern for fintech companies, and allows users to operate in low or moderate internet connections as well. Edge computing improves real-time processing, enhancing the performance of applications and services, especially where latency is low.
AI-Driven Cloud Solutions
AI-infused cloud computing refers to the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies into cloud computing platforms and services to enhance their efficiency, functionalities, capabilities, etc. These solutions leverage AI and machine learning algorithms to automate tasks, analyze data, improve decision-making, and optimize cloud resources.
Along with it, AI algorithms analyze historical data and real-time metrics to predict trends and potential issues in cloud infrastructure. The practice helps prevent downtime, improve performance, identify issues early, and reduce operational risks.
DevSecOps Security Integrations
DevSecOps, which stands for ‘Development, Security, and Operations’ is an approach to software development and tech operations, emphasizing and integrating security practices throughout the software development cycle.
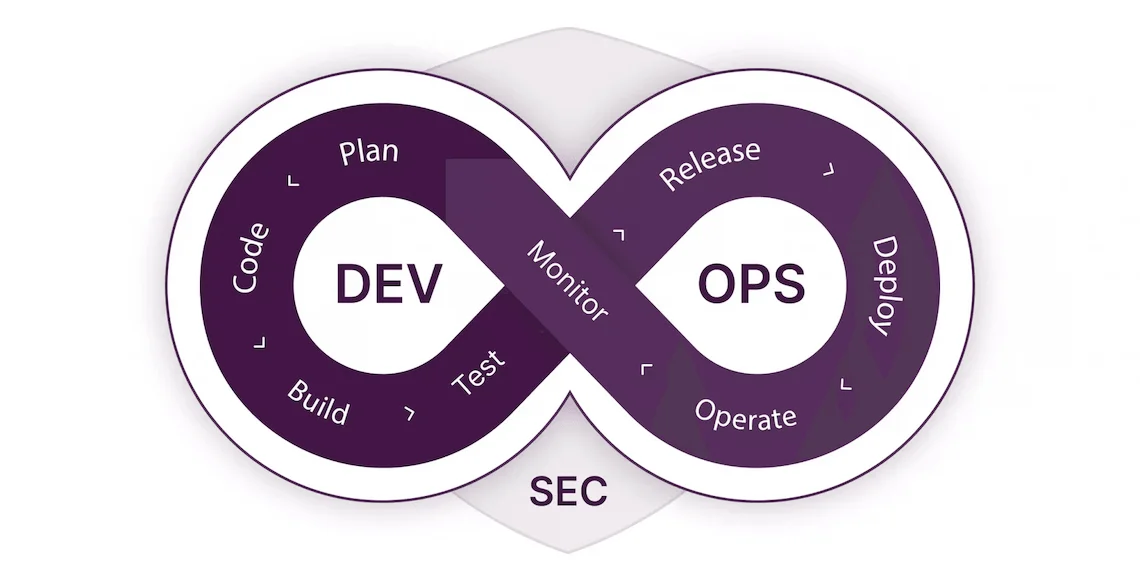
In the context of cloud computing, DevSecOps refers to incorporating security measures, practices, and tools in stages of the cloud app development, deployment, and integration process. It encourages shifting left security practices, automated security practices, container security, continuous compliance, identity and access management, etc.
In a nutshell, DevSecOps helps fintech organizations build and operate secure and resilient cloud applications, reducing the risk of security breaches and vulnerabilities in the cloud computing environment.
Read also: The Differences Between DevOps and DevSecOps: An In-depth Guide
What are the Challenges Associated with Cloud Solutions Adoption?
No doubt, cloud computing offers numerous benefits that are hard to count on fingers. However, like other technologies, it also has complications and challenges that fintech companies might face during the adoption. Below listed are some of the most common challenges connected to cloud computing adaptation.
Security Risk
In cloud computing, there is an underlying security risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and data loss. Moreover, cloud providers may store data in multiple geographic locations, which creates the issue of unethical use, data sovereignty, and handling.
Compliance Issues
Compliance with regulatory requirements is another matter of concern. Cloud services offer compliance certification to tackle the issue. However, the certificate may create trouble for fintech organizations and call for legal and financial repercussions if it is not aligned with regulations like GDPR, PCI PSS, etc.
Cloud Cost Management
Without careful monitoring and control, cloud expenses may rise quickly and lead to budget overruns, causing losses rather than profits. Choosing cloud type, understanding the pricing model, budgeting, resource tagging, and resource distribution are some other adoption challenges of cloud computing for fintech companies.
Vendor Lock-In
The issue comes into the picture when fintech companies largely depend on particular cloud providers’ services and technologies. In this scenario, migrating applications and data from one provider to another can be troublesome, expensive, and disruptive.
Performance and Latency
Data travels long distances between the cloud and end-users that can lead to latency, network performance issues, delays, impacting application responsiveness, etc. Fintech organizations can frequently face these issues if they don’t choose the cloud region strategically and consider content delivery networks (CDNs) properly.
Availability and Downtime
Cloud service providers may experience outages that can disrupt business operations. They might face downtime and service interruptions if they fail to implement redundancy and failover mechanisms.
Data Handling and Control
Moving to the cloud may result in a perceived loss of control over infrastructure and data. In the absence of established governance policies and restricted control, fintech organizations may face troubles like unethical use of data, unauthorized access, and security breaches.
Lack of Expertise and Knowledge
The ecosystem of cloud computing is complicated and evolves with time continuously. Many organizations lack the necessary expertise and knowledge to manage cloud environments effectively. The cloud demands specialized skills for managing tasks related to cloud architecture, security, networking, and cloud-native development. In the absence of a skilled workforce, fintech organizations can encounter severe losses during cloud adoption.
Successful adoption of cloud computing is a crucial part of the process and requires careful planning, ongoing monitoring, and adapting to the evolving cloud landscape. You must hire a reputed organization providing cloud services using the best practices and technical solutions while mitigating potential risks.
Empower Your Fintech Business Using Cloud Solutions With MindInventory
MindInventory is a reputed organization supporting the fintech industry to adopt cloud computing and other trending technologies. We have a professional team to design and implement robust security measures, ensuring compliance with financial regulations like PCI DSS, GDPR, etc., and proactively addressing security threats and vulnerabilities.
Our organization facilitates various cloud computing services to fintech companies, including cloud app development, configuration, architecting, integration, security deployment, serverless computing, cloud migration, etc. We also provide dedicated cloud support and consultation to help them choose the right cloud type and provider.
Our experts understand the intricacies of data protection and privacy laws and handle sensitive data with utmost responsibility. They also assess and mitigate associated risks and make sure you get maximum benefits from cloud adaptation.

FAQ on Cloud Computing
With cloud computing, fintech companies can quickly develop, test, and deploy new financial products and services while maintaining their existing business data on remote servers. The technology introduces agility, scalability, and cost-efficiency, allowing fintech firms to innovate and compete in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Companies like Moneybox, Albaco, Capital on Tap, KPMG, Auka, Goldman Sachs, FaceBook, Intel, Yahoo, Cred, Axis Bank, Paytm, Upstox, etc., are using cloud computing to store and maintain their data. These are just a few examples of it. The list is very long, as many fintech companies are adapting clouds.
The choice of cloud provider relies on your business requirements, storage space, and cloud types. You can choose from private, public, hybrid, or multi-clouds. However, we advise you to analyze your requirements and compare all providers before finalizing the one. You can connect with the MindInventory team and seek expert consultation. We will help you make a better choice.
Cloud computing is cost-effective and saves companies from investing in on-premises infrastructure. Cloud enhances agility and innovation, allowing banks and other financial institutes to develop and deploy new services or products rapidly. Uptight security and proper maintenance are also the prime reasons behind this shift. Hence, fintech firms can seamlessly scale up or scale down their business while ensuring optimal performance and avoiding over-provisioning.













